What/who/why are Process Models? 🤔
What ->A framework for the activities, actions, and tasks that are required to build high-quality software. It is an adaptable approach that enables the people doing the work to pick and choose the appropriate set of work actions and tasks. Software process defines the approach that is taken as software is engineered.
Who -> Software engineers and their managers, clients also. People adapt the process to their needs and follow it.
Why -> Provides stability, control, and organization to an activity that can if left uncontrolled, become quite chaotic. However, modern software engineering approaches must be agile and demand only those activities, controls, and work products that are appropriate.
- Purpose of the process is to deliver software promptly and with sufficient quality to satisfy those who have sponsored its creation and those who will use it.
Five Activities of a Generic Process Framework ✋
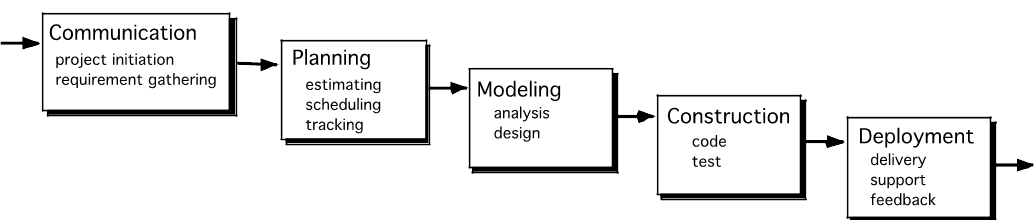
- Communication: Communicate with customers to understand objectives and gather requirements.
- Planning: Creates a “map” that defines the work by describing the tasks, risks, resources, work products, and work schedule.
- Modeling: Create a “sketch”, of what it looks like architecturally, how the constituent parts fit together, and other characteristics.
- Construction: Code generation and testing.
- Deployment: Delivered to the customer who evaluates the products and provides feedback based on the evaluation.
These five framework activities can be used for all software development. For many software projects, these framework activities are applied iteratively as a project progresses.
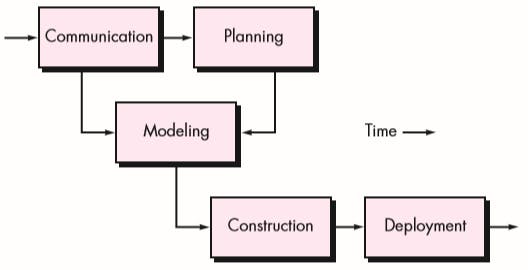
Process Flow
It is a diagrammatic representation of the flow and exchange of information within a system.
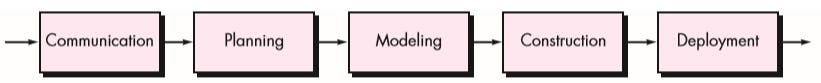
Linear Process Flow
A linear process flow executes each of the five framework activities in sequence, beginning with communication and culminating with deployment.
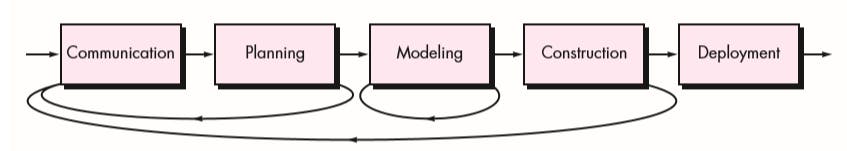
Iterative Process Flow
An iterative process flow repeats one or more of the activities before proceeding to the next.
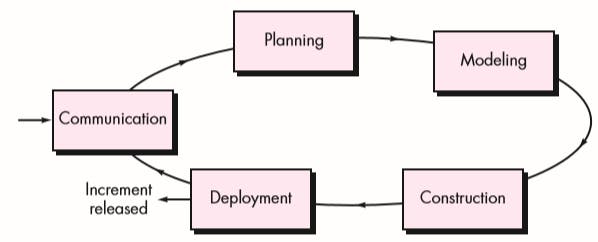
Evolutionary Process Flow
An evolutionary process flow executes the activities in a circular manner.
Parallel Process Flow
A parallel process flow executes one or more activities in parallel with other activities.
Waterfall Model 🌊
- It is very simple but idealistic.
- Earlier this model was very popular but nowadays it is not used.
- It is very important because all the other software development models are based on the waterfall model.
- This model considers that one phase can be started after completing the previous phase. i.e The output of one phase will be the input to the next phase.
- The development process can be considered as a sequential flow.
Advantages of Waterfall Model
- This model is very simple and easy to understand.
- Phases in this model are processed one at a time.
- This model works well for smaller projects and projects where requirements are well understood because need very few resources.
- It is a sequential model.
- There is no scope of phase overlap here as you cannot proceed to the next phase until you finish the earlier phase.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Model
- It is not very flexible.
- It takes a lot more time.
- It is difficult to estimate time and cost.
- It does not incorporate any mechanism for error correction because It assumes that no error is ever committed by developers during any phase.
- It is difficult to take any change requests after the requirements specification phase is complete.
Evolutionary Models
Usually, a set of the core product or system requirements is well understood, but the details and extensions have yet to be defined. That's why We need a process model that has been explicitly designed to accommodate a product that evolved over time. Therefore, Two new models are introduced, namely Spiral and Prototyping models.
The Spiral Model 🌀
- One of the most important Software Development Life Cycle models, which provides support for Risk Handling.
- It couples the iterative nature of prototyping with the controlled and systematic aspects of the waterfall model.
- In its diagrammatic representation, it looks like a spiral with many loops.
- The exact number of loops of the spiral is unknown and can vary from project to project.
- Each loop of the spiral is called a Phase of the software development process.
- The exact number of phases needed to develop the product can be varied by the project manager depending on the project risks.
- The project manager has an important role to develop a product using the spiral model, As the project manager dynamically determines the number of phases.
- The Radius of the spiral at any point represents the expenses(cost) of the project so far, and the angular dimension represents the progress made so far in the current phase.
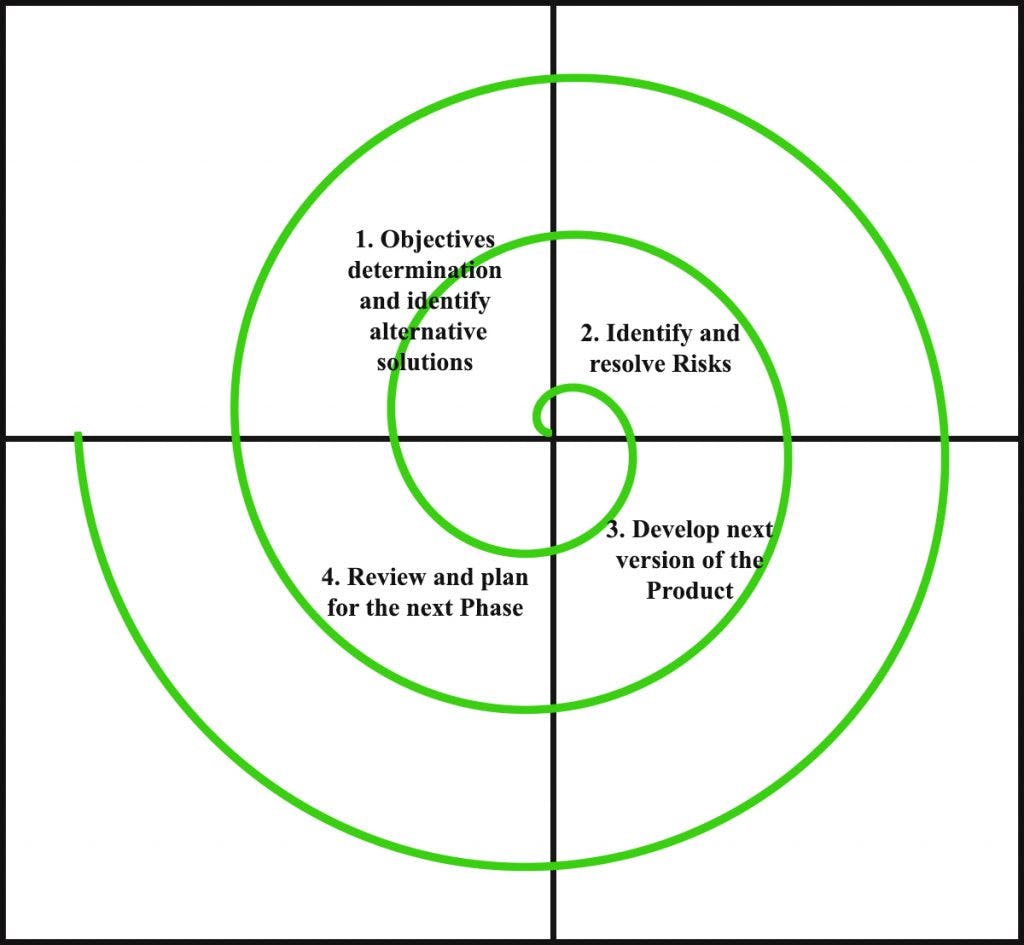
Risk Handling-> A risk is any adverse situation that might affect the successful completion of a software project.
When to use Spiral Methodology? 🤔
- When a project is large, releases are required to be frequent.
- When the creation of a prototype is applicable, risk and cost evaluation is important.
- When requirements are unclear, complex and changes may require at any time.
- For medium to high-risk projects.
Advantages of Spiral Model
- Risk Handling
- Good for large projects
- Flexibility in Requirements
- Customer Satisfaction
Disadvantages of Spiral Model
- Complex
- Expensive
- Too much dependability on Risk Analysis
- Difficulty in time management
The Prototyping Model 🅿️
- The Prototyping Model is one of the most popularly used Software models.
- This is used when the customers do not know the exact project requirements beforehand.
- In this model, a prototype of the end product is first developed, tested, and refined as per customer feedback repeatedly till a final acceptable prototype is achieved which forms the basis for developing the final product.
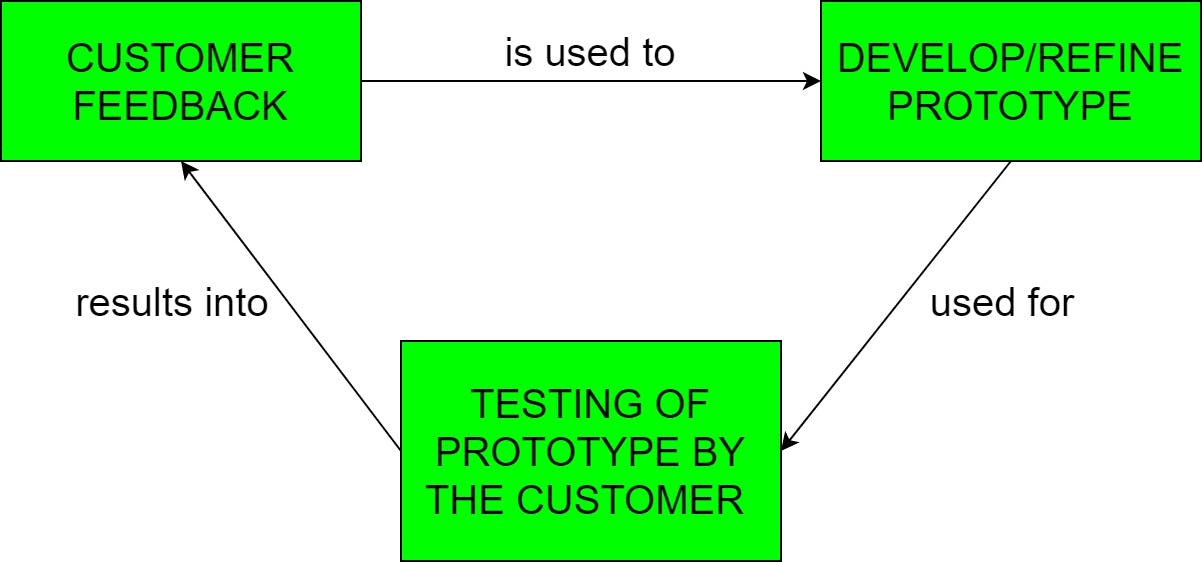
- Users get a feel for the actual system, and developers get to build something immediately.
When to use the Prototype Model? 🤔
The Prototyping Model should be used when the requirements of the product are not clearly understood or are unstable. It can also be used if requirements are changing quickly.
Advantages of Prototype Model
- Users are actively involved in the development.
- New requirements can be easily accommodated.
- Missing functionalities can be easily figured out.
- Errors can be detected much earlier.
- Flexibility in design.
- The developed prototype can be reused.
Disadvantages of Prototype Model
- Costly w.r.t time as well as money.
- Poor Documentation due to continuously changing customer requirements.
- It is very difficult for developers to accommodate all the changes demanded by the customer.
- This methodology may increase the complexity of the system as the scope of the system may expand beyond the original plans.
- The customer might lose interest in the product if not satisfied with the initial prototype.
Agile Software Development / Model
What is "Agility"? 🤨
- Agility means effective (rapid and adaptive) response to change, and effective communication among all stockholders.
- Drawing the customer onto the team and Organizing a team so that it is in control of the work performed.
Agility and the Cost of Change
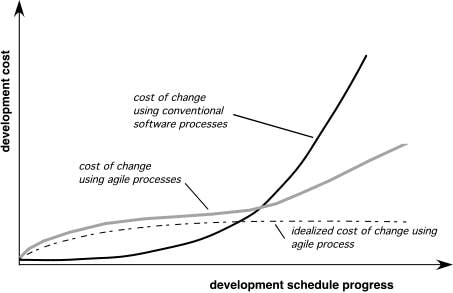
An Agile Process
- Is driven by customer descriptions of what is required / People-based rather than plan-based methods.
- The agile process forces the development team to focus on the software itself rather than design and documentation.
- The agile process believes in the iterative method.
- The aim of the agile process is to deliver the working model of software quickly to the customer.
- Adapts as changes occur.
Agile model is the combination of iterative and incremental process models.
Principles of Agile model
- Highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- It welcomes changing requirements, even late in development.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference for the shortest timescale.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Simplicity – the art of maximizing the amount of work not done – is essential.
- The process molds to the needs of the people and team, not the other way around.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
That's why During the Lockdown period companies preferred to do Video-conferences to keep you updated with your work/tasks rather than handing out written tasks & goals.
Advantages of Agile model
- Working through Pair programming produces well-written compact programs.
- It reduces the total development time of the whole project.
- Customer representatives get the idea of updated software products after each iteration. So, it is easy for him to change any requirement if needed.
Disadvantages of Agile model
- Lack of formal documents, creates confusion.
- Maintenance of the developed project can become a problem, due to the absence of proper documentation.
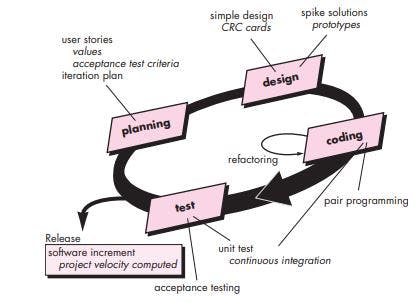
Extreme Programming (XP) ❌🅿️
- Extreme programming (XP) is one of the most important software development frameworks of Agile models.
- The extreme programming model recommends taking the best practices that have worked well in the past in program development projects to extreme levels.
- Good practices need to be practiced in extreme programming.
Basic Principles
- Through frequent iterations, the developers implement User Stories.
- Agile team assesses each story and assigns a cost.
- Stories are grouped to form a deliverable increment.
- A commitment is made on the delivery date.
- After the first increment project velocity is used to help define subsequent delivery dates for other increments.
User stories are simple and informal statements of the customer about the functionalities needed.
Basic Activities
- Coding:
- Recommends the construction of a unit test for a store before coding commences.
- The coding activity includes modeling that will be transformed into code, scripting a web-based system, and choosing among several alternative solutions.
- Encourages pair programming.
- Testing:
- The XP model gives high importance to testing and considers it to be the primary factor to develop fault-free software.
- All unit tests are executed daily.
- Acceptance tests are defined by the customer and executed to assess the customer's visible functionality.
- Designing:
- Follows the KIS principle.
- Encourage the use of CRC cards (Class Responsibility Collaborator).
- For difficult design problems, suggests the creation of spike solutions.
- Encourages refactoring.
Spikes are used to investigating a concept and/or create a simple prototype.
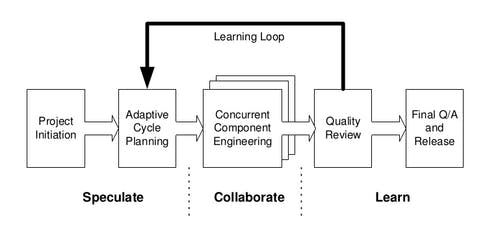
Adaptive Software Development
- Mission-driven planning.
- Component-based focus.
- Uses time-boxing.
- Explicit consideration of risks.
- Emphasizes collaboration for requirements gathering.
- Emphasizes learning throughout the process.
V-Model ✌️
- The process executes in a sequential manner in V-shape.
- It is also known as the Verification and Validation model.
- Development of each step is directly associated with the testing phase.
- The next phase starts only after the completion of the previous phase.
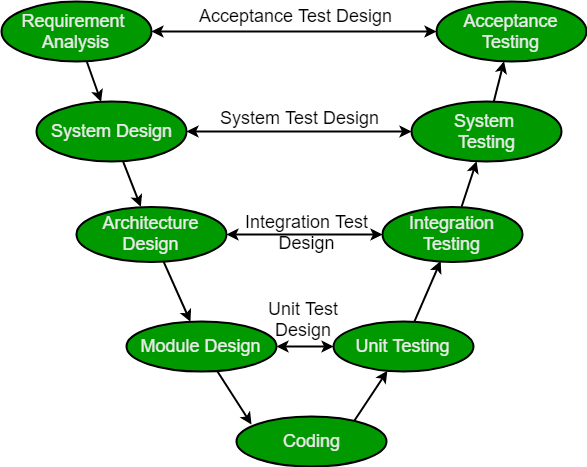
- Verification:
- It involves a static analysis technique done without executing code.
- It is the process of evaluation of the product development phase to find whether specified requirements meet.
- Validation:
- It involves a dynamic analysis technique, and testing is done by executing code.
- It is the process to evaluate the software after the completion of the development phase to determine whether the software meets the customer's expectations and requirements.
When to use the V-Model? 🤔
- Where requirements are clearly defined and fixed.
- When ample technical resources are available with technical expertise.
Advantages of V-Model
- This is a highly disciplined model and Phases are completed one at a time.
- Simple and easy to understand and use.
- This model focuses on verification and validation tasks early in the life cycle, increasing the likelihood of producing an error-free and good-quality product.
- It enables project managers to track progress accurately.
Disadvantages of V-Model
- High risk and uncertainty.
- It is not good for complex and object-oriented projects.
- It does not easily handle concurrent events.
Thank you so much for taking your valuable time for reading.
I took the initiative to learn in public and share my work with others. I tried my level best in squeezing as much information as possible in the easiest manner. Hope you learnt something new today :)
In the next part of this blog, we will study about Software Testing and Debugging.
Any feedback for further improvement will be highly appreciated!