What Is YAML?
YAML is the abbreviated form of “YAML Ain’t markup language” and is a data serialization language often used to create configuration files with any programming language. You might call this a dictionary, hash, or data object, depending on your programming language or mood.
- The basic structure of a YAML file is a map.
- It is a strict superset of JSON.
- It is a Data serialization language similar to XML or JSON.
- It is mostly used for storing configuration information.
- YAML files store data objects, and they do not include commands and instructions.
- Previously, stood for Yet Another Markup Language.
- The files should have .yaml or .yml as the extension.
- YAML does not allow the use of tabs while creating YAML files; spaces are allowed instead.
Data Serialization
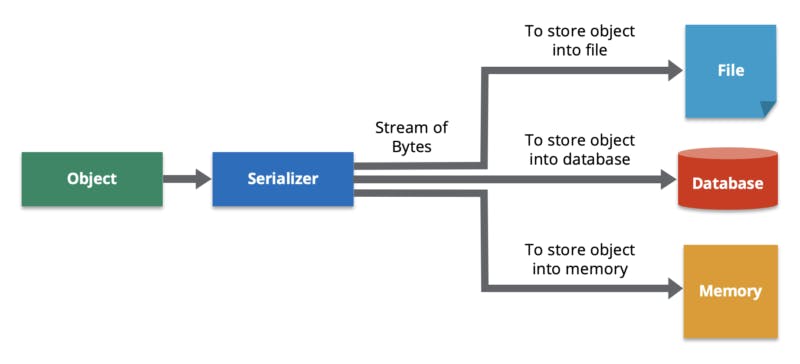
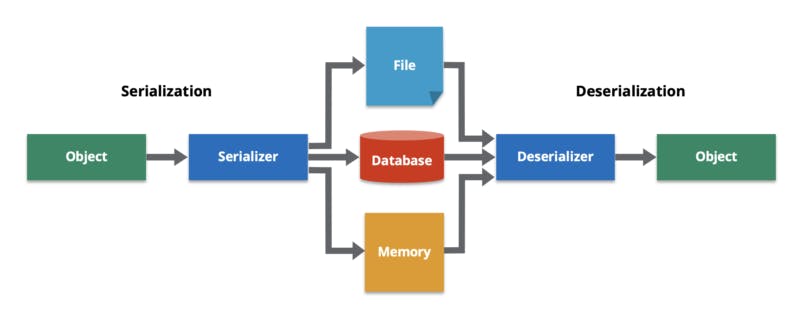
Data serialization is the process of converting data object or object states that is present in complex data structures, into a stream of bytes for storage, transfer, and distribution in a form that can allow recovery of its original structure.
De-serialization
The reverse process of data serialization is known as Data De-serialization.
What is YAML used for?
- YAML is most commonly used to create configuration file.
- YAML is used for Kubernetes resources and deployments.
- Configuration files are recommended to be written in YAML rather than JSON.
- YAML has better readability and is more user-friendly.
- YAML files can be added to source control, such as Github, so that changes can be tracked and audited.
Benefits of YAML
- Simple and clean syntax
- Easy to implement and use
- Strict syntax
- Version control friendly
- More powerful when representing complex data
- Matches native data structures of modern programming languages
- Consistent/compatible with various tools
- Unambiguously specifies the data structures of the serialized data
- Fast
Basic Components of YAML File
Conventional Block Format
This block format uses hyphen+space to begin a new item in a specified list.
---
# Favorite movies
- The Great Gatsby
- Shutter Island
- Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind
Inline Format
Inline format is delimited with commas and space and the items are enclosed in JSON.
---
# Shopping list
[milk, groceries, eggs, juice, fruits]
Folded Text
Folded text converts newlines to spaces and removes the leading whitespace.
---
- {name: Kunal Singh, age: 21}
- name: Sachin Sharma
age: 22
YAML Character & Functionality
- ? -> It denotes a mapping key
- : -> It denotes a mapping value
- _ -> It denotes a block sequence entry
- [, ] -> Start and End of a flow sequence
- {, } -> Starts and Ends a flow mapping
- # -> It denotes the comments
- ! -> It denotes node's tag
- | -> It denotes literal block scalar
- > -> It denotes a folded block scalar
- % -> It denotes the directive use
You can check the examples for the above-given character in Datatypes.
YAML Datatypes
Key-Value Pairs and Dictionaries
- The key value is YAML's basic building block
- YAML document is a member of at least one dictionary
- The key is always a string
- The value can be of any datatype
Numeric types
zero: !!int 0
positiveNum: !!int 44
negattiveNum: !!int -44
binaryNum: !!int 0b11011
octalNum: !!int 0654
hexaNum: !!int 0x45
commaValue: !!int +540_000 # 540,000
exponentialNumbers: 6.023E56
Not-A-Number (NAN) or Infinity
--- num: .inf nan: -.inf infinite: .NAN
Strings
- In YAML strings are Unicode. Mostly, you don't have to specify them in quotes.
---
type: this is a normal string
But if we want escape sequences handled, we need to use double quotes.
---
pow: "this is not a normal string\n"
siuu: this is not a normal string\n
YAML processes the first value as ending with a carriage return and linefeed. Since the second value is not quoted, YAML treats the \n as two characters.
pow: this is not a normal string
siuu: this is not a normal string\n
- YAML will not escape strings with single quotes, but the single quotes do avoid having string contents interpreted as document formatting. String values can span more than one line. With the fold (greater than) character, you can specify a string in a block.
siuu: >
this is not a normal string it
spans more than
one line
see?
But it's interpreted without the newlines.
siuu: this is not a normal string it spans more than one line see?
The block (|) character has a similar function, but YAML interprets the field exactly as is.
bar: |
this is not a normal string it
spans more than
one line
see?
But in its Interpretation, we see the new lines where they are in the document.
bar: this is not a normal string it
spans more than
one line
see?
Nulls
You enter nulls with a tilde or the unquoted null string literal.
---
pow: ~
siuu: null
Booleans
YAML indicates boolean values with the keywords True, On, and Yes for true. False is indicated with False, Off, or No.
---
pow: True
siuu: False
machine: On
light: Off
Arrays
You can specify arrays or lists on a single line.
items: [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
names: [ "one", "two", "three", "four" ]
Or, you can put them on multiple lines.
items:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
names:
- "one"
- "two"
- "three"
- "four"
Dictionaries
You can put dictionaries inline.
---
pow: { name1: nuey, name2: aomine, name3: akaza }
They can be nested and hold any value.
---
poe:
siuu:
- flap
- blap
- clap
YAML for Kubernetes
Kubernetes works based on actual state and defined state. Kubernetes resources, such as pods, objects, and deployments can be created using YAML files. Developers specify the defined state using the YAML or JSON files they submit to the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes uses a controller to analyze the difference between the newly defined state and the actual state in the cluster.
There is more to YAML for Kubernetes.
Thank you so much for taking your valuable time to read
Inspired by Kunal Kushwaha and his tutorials, I took the initiative to learn in public and share my work with others. I tried my level best in squeezing as much information as possible in the easiest manner. Also, Thank you Saiyam Pathak for amazing DevOps roadmap.
Hope you learned something new today :)
Resource Link:
Any feedback for further improvement will be highly appreciated!
